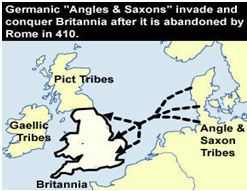
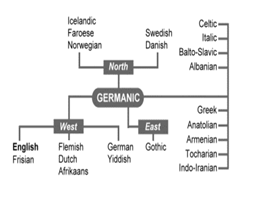
English language’s history began with the coming of the Germanic tribes (the Angles, the Saxons and the Jutes) who attacked Britain during the fifth century AD. At the time, British residents’ language was the Celtic language. The Angles derived from "Englaland" and their language was known as "Englisc" out of which the two words “England” and “English” are derived.
Old English
The Germanic tribes who invaded Britain spoke the same language which reclaimed later on, in the same place they attacked, into the so-called “Old English”. Old English varies considerably from the English we use nowadays. Today, native English speakers have a remarkable difficulty comprehending Old English. Yet, the majority of the current English words used today have old roots. For example, verb “To be”, “Beam” and “Strong” not only hold the same meaning of today but we can also find them in the Old English. The most significant work of old English literature is the oldest surviving epic poem “Beowulf” (fig3) which is written in Old English. Old English was used until 1100.
Middle English
William the Conqueror, the Duke of Normandy (France), invaded England in 1066. The new invaders came and brought with them the French language which became later on the language of the ruling court, and the business and ruling classes. So, there was a linguistic rank partition, lower classes spoke English and upper classes spoke French. It was until the 14th century that English became prevalent again with some French words. The Middle English language is the language of the greatest English poet Geoffrey Chaucer (fig4) (1343 – 25 October 1400), who is also known as the father of English literature. Like the Old English, the Middle English is very difficult to be understood by the native speakers today.
Modern English
Early Modern English
The Early Modern English started with an unexpected and a notable shift in the pronunciation, where the vowels being pronounced shorter and shorter. By the 16th century, many people from the entire world visited Britain. In addition, the Renaissance took part in the entrance of new vocabularies into the English language. Printing also participated in spreading the concept of the common language and standardisation. As a result, books became cheaper and people could have access to them. Spelling and Grammar became determined, and the London’s dialect, where a great number of publishing houses, became the standard dialect. Moreover, the English dictionary was first published in 1604.
Late Modern English
The most important variety between Early Modern English and Late Modern English is “Vocabulary”. Late modern English is richer in vocabulary thanks to the Industrial Revolution (1760) and technology which was a push factor for creating new words in order to find new ways of representing new concepts and the words in English which are mainly borrowed from another language.
Varieties of English
The American variety of English was a result of the English colonization of North America in 1600. In addition, Spanish had an effect on American English thanks to the settlement of the American West. American English also influenced by French and West African words.
Chronology
RESIDENTS WHO SPEAK CELTISH
55 BC: Roman invasion of Britain by Julius Caesar
AD 43: Roman invasion and occupation.
Beginning of Roman rule of Britain
463: Roman withdrawal from Britain
449: Settlement of Britain by Germanic invaders
OLD ENGLISH
450-480: Earliest known Old English inscriptions
1066: William the Conqueror, Duke of Normandy, invades and conquers England
MIDDLE ENGLISH
C 1150: Earliest surviving manuscripts in Middle English
1348: English replaces Latin as the language of instruction in most schools
1362: English replaces French as the language of the law. English is used in Parliament for the first time.
1388: Chaucer starts writing The Canterbury Tales.
C 1440: The Great Vowel Shift begins
EARLY MODERN ENGLISH
1476: William Caxton establishes the first English printing press
1564: Shakespeare is born
1604: Table Alphabetical, the first English dictionary, is published
1607: The first permanent English settlement in the New World (Jamestown) is established
1616: Shakespeare dies
1623: Shakespeare's First Folio is published
1702: The first daily English-language newspaper, The Daily Courant, is published in London
1755: Samuel Johnson publishes his English dictionary
1776: Thomas Jefferson writes the American Declaration of Independence
1782: Britain abandons its colonies in what is later to become the USA
LATE MODERN ENGLISH
1828: Webster publishes his American English dictionary
1922: The British Broadcasting Corporation is founded
1982: The Oxford English Dictionary is published
How English became a global language
What is a global language?
In our increasingly changing world, a global language, a language that is learned and spoken internationally, is becoming more and more a must. In the past, there were many obstacles like religion and likes. But with the technologies, this is not a problem anymore, it’s about communication. And the question is which language is the most appropriate to use in talking with others and they can understand us no matter from which country he/she is. In order for a language to become a global and influential language, there must be a combination of three main points which are; how many countries are using that language as their mother tongue, how many countries are adopting it as their official language and the number of countries that are using it at schools. In addition, the structural qualities of that language and its vocabulary and literature throughout history and its relation with the other languages or cultures and, of course, its popularity. Moreover, technological, economic and political powers are able to maintain the enlargement of a language.
Is English a global language?
There has never been a language more widespread throughout history like English. Its wide use in the fields of academics, business, art, science, education, transportation, politics and entertainment is a plus for it. About nearly 85 % of international organization use English as an official language, and about 1/3 of international organization including OPEC (Organization of the Petroleum Exporting Countries), EFTA (European Free Trade Association) and ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) use English only. American economic and cultural dominance, in films, television, music, business and finance has consolidated English to maintain it today. Researcher David Graddol says two billion people will be learning English as it becomes a truly "world language".
There are many linguistic features that make English likely to be a global language, like;
· The fullness of English vocabulary: Oxford is the world’s largest dictionary.
· English is a flexible language. We can use the same word both as a verb and a noun. Yet, new words can be made easily.
· Simple grammar.
· Easy in terms of pronunciation and spelling.
· The literature quality. It has proved its superiority and richness through history.
What about the future?
Will English always remain number one? This is the question that many linguists ask. When we look back in history, we find that Latin was almost influential the same way as English today and was learnt for the same reasons as English today. Yet, Latin is no longer used or spoken nowadays. The need for a new global language changes over time and this depends of course on the political and economic powers of the countries. But we can ensure that English will remain powerful during our lifetime.